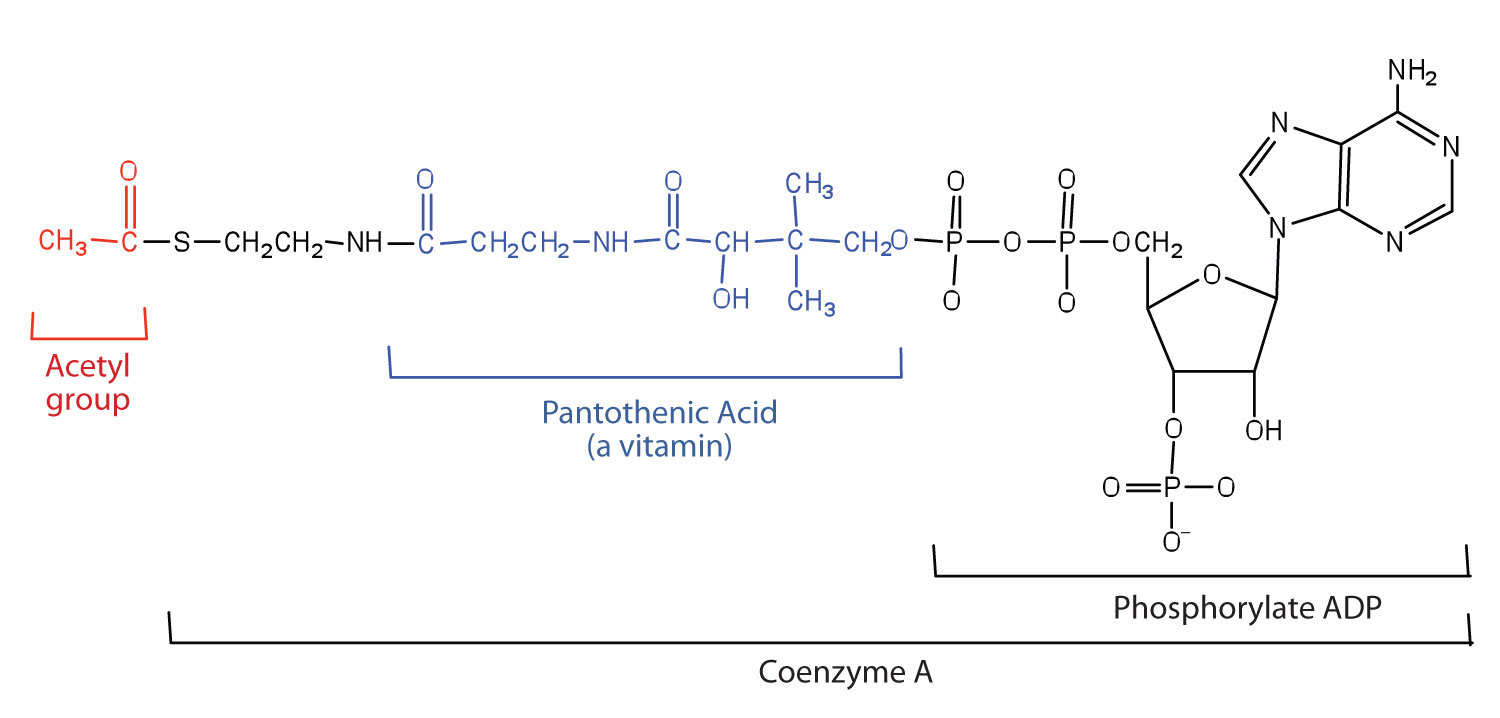
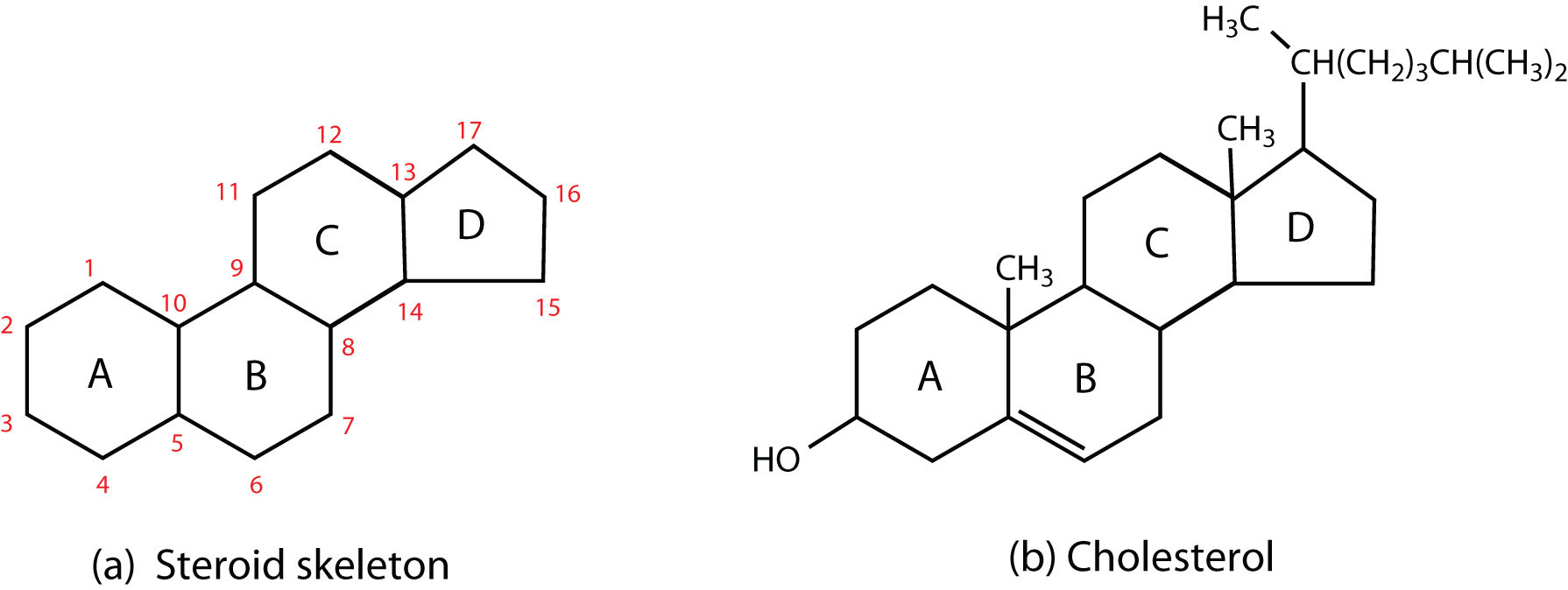
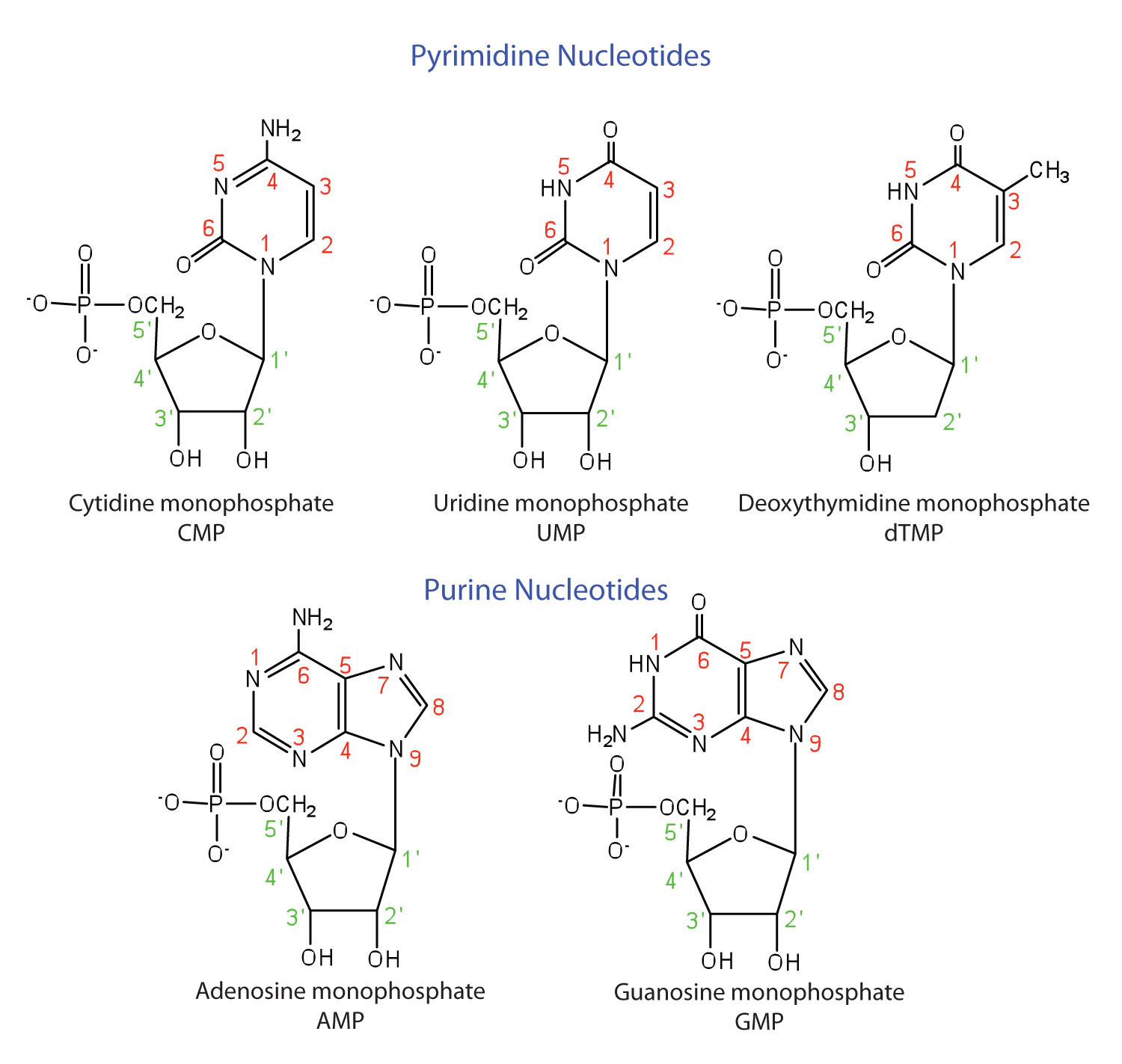
Introduction to organic chemistry
Data: 4.03.2018 / Rating: 4.7 / Views: 650Gallery of Video:
Gallery of Images:
Introduction to organic chemistry
Introduction To Organic Chemistry. Admin February 7, 2016 Igcse Chemistry Revision Notes, O Level Chemistry Revision Notes 1 Comment. Homologous Series: A set of organic compounds with similar chemical properties, with a general formula and showing a gradation in physical properties as a result of increase in the size of mass of the molecule. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon, an element that forms strong chemical bonds to other carbon atoms as well as to many other elements like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and the halogens. Because of its versatility in forming covalent bonds, more than a million carbon compounds are known. Organic chemistry is all about carbon. Any chemical compound that contains carbon atoms can be called an organic compound but it usually means compounds with a carbon chain of some sort. Any chemical compound that contains carbon atoms can be called an organic compound but it usually means compounds with a carbon chain of some sort. Introduction to Organic Chemistry Chem. Substances p3 An Introduction to Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of carbon containing compounds and their properties. Organic chemistry is the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carboncontaining compounds, which include not only hydrocarbons but also compounds with any number of other elements. Carbon atoms can bond with other carbon atoms to form an enormous range of compounds with different carbonchain lengths. The simplest organic compounds are a family of saturated hydrocarbons called the alkanes, shown below. The Introduction to Organic Chemistry chapter of this College Biology Help and Review course is the simplest way to master introductory organic chemistry. Introduction to Organic Chemistry BIOB111 CHEMISTRY BIOCHEMISTRY Session 7. Key concepts: session 7 From this session you are expected to develop an understanding of the following concepts: Concept 1: Organic compounds Concept 2: Organic vs inorganic compounds Concept 3: Individual atoms vs atoms within a compound Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that is concerned with the study of carbon containing compounds. Carbon possesses a unique property of catenation. Catenation refers to the linkage of atoms of same element to form longer chains. Thus, these form longer pp sigma bond while in heavy. CliffsNotes study guides are written by real teachers and professors, so no matter what you're studying, CliffsNotes can ease your homework headaches and help you score high on exams. The word Organic is one of the most overused in the English language. People use it as a derogatory term in phrases like Don't eat that; it's not organic. Of course, there is a precise scientific definition of the word. What is Organic Chemistry All About? Which people are the best to interact with first? Which will be the most important to know in the long run. Introduction to Organic Chemistry is most suited for a onesemester organic chemistry course. It is designed for students who require the fundamentals of organic chemistry as a. Introduction to Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition provides an introduction to organic chemistry for students who require the fundamentals of organic chemistry as a requirement for their major. It is most suited for a one semester organic chemistry course. In an attempt to highlight the relevance of the material to students, the authors place a. Introduction to Chapter 1: Pain, pleasure, and organic chemistry: capsaicin and vanillin Contributors Chapter 1 now matches the updated (2016) edition of Organic Chemistry With a Biological Emphasis. Introduction to Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition provides an introduction to organic chemistry for students who require the fundamentals of organic chemistry as a requirement for their major. It is most suited for a one semester organic chemistry course. In an attempt to highlight the relevance of the material to students, the authors place a strong emphasis on showing the interrelationship. This text presents a treatment of aromatic chemistry allowing for continuity in the coverage of the aromatic ring and aliphatic and aromatic amines; covers spectroscopy and carbon nuclear resonance; provides a review of basic chemistry and an organic reactivity review which covers acids and bases and coverage of DNA, catalytic antibodies and environmental issues. Introduction to Organic Semiconductors Using Accessible Undergraduate Chemistry Concepts Kevin L. Ratner Department of Chemistry, Northwestern University, 2145 Sheridan Road, Evanston, Illinois, United States CHAPTER 14: An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 14. 3 Isomerism Learning outcomes: (a) interpret, and use the general, structural, displayed and skeletal formulae of the following Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. It is such a complex branch of chemistry because carbon form a wide variety of compounds for the following reasons These are the key definitions used for this topic, with two activities a cloze and matching title with definition. The cloze was made in Cloze Pro and I am unable to load the file on to this website. If you do have Cloze Pro product I am happy to send. Let us start with the question What is Organic chemistry? The simple answer is: It is the chemistry of carbon containing compounds, which are otherwise known as organic compounds. So it is pretty easy to recognize that we should start our journey of organic chemistry by exploring the chemical nature of carbon. An Introduction to Organic Chemistry 82 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon with the exception of simple compounds e. carbonates (CO 3 2), carbon dioxide (CO 2) and carbon monoxide (CO). Nomenclature There are over 6 million known organic These are the homework exercises to accompany Chapter 1 of the Textmap for Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry (Roberts and Caserio). This video tutorial provides an introduction or basic overview on what you will learn in your first college semester of organic chemistry. INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is a chemistry of carbon compounds. Example: methane, DNA, urea, DDT (insecticide), penicillin, nicotine, aspirin etc. But not all carbon compounds are organics. Inorganic chemistry is the study of the synthesis, reactions, structures and properties of compounds of the elements. This subject is usually taught after students are introduced to organic chemistry, which concerns the synthesis and reactions of compounds of carbon (typically containing CH bonds). Organic chemistry is the study of the chemistry of carbon compounds. A functional group is a specific structural arrangement of atoms or bonds that imparts a characteristic chemical reactivity to the molecule; alcohol group and carboxylic group (answers will vary). Can you find your fundamental truth using Slader as a completely free Introduction to Organic Chemistry solutions manual? Now is the time to redefine your true self using Sladers free Introduction to Organic Chemistry answers. Introduction to Organic Chemistry has 7 ratings and 1 review. This text presents a treatment of aromatic chemistry allowing for continuity in the coverag CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. 1 Historical Background of Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the area of chemistry that involves the study of carbon Center for Academic Resources Smith Hall, Second Floor 3 Garrison Avenue Durham, New Hampshire contact webmaster (603) cfar. edu Organic chemistry is the chemistry subdiscipline for the scientific study of structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials (materials that contain carbon atoms). Study of structure determines their chemical composition and formula. Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Part I Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbons are molecules that contain only hydrogen and carbon atoms Each Carbon atom forms 4 bonds and each hydrogen forms 1 bond Introduction Biochemistry is the chemistry of living things. Here we talk about the basics of Organic Compounds, Homologous Series and Functional Groups. Chapter 5 Introduction to Organic Chemistry This content can also be downloaded as Interactive PDF. For the interactive PDF, adobe reader is required for full functionality. This text is published under creative commons licensing, for referencing and adaptation, please click here. 1 Pain, pleasure, and organic chemistry 5. 2 Drawing organic molecules Finding the [ Organic chemistry studies carbonbased substances. Carbon, as described in more detail in this book, has unique properties that allow it to make complex chemicals, including those of living organisms. In organic chemistry, it is important to know about electrons, mechanisms, resonance, and delocalization. To learn organic chemistry, a student must learn the terminology, functional groups, nomenclature, electrons, and mechanisms. Introductory text for a short course in organic chemistry. Abstract: The sixth edition of Morrison and Boyd's text can trace its origin back to 1958. The new edition follows in the footsteps that made the earlier editions the standard in the field for the sophomore oneyear organic courses for many years. The Department of Chemistry at MIT is one of the nation's top chemistry departments. It has an illustrious history in sharing the MIT tradition of excellence, and it has provided national leadership in chemical education and research throughout the century. Organic chemistry is important because it is the study of life and all of the chemical reactions related to life. Several careers apply an understanding of organic chemistry, such as doctors, veterinarians, dentists, pharmacologists, chemical engineers, and chemists. Get started learning about the study of matter. These lecture notes, study guides, lab experiments, and example problems can help you understand the building blocks of life. A brief introduction to organic chemistry Carbon can form covalent bonds with itself and other elements to create a mindboggling array of structures. In organic chemistry, we will learn about the reactions chemists use to synthesize crazy carbon based structures, as well as the analytical methods to characterize them. The purpose of this Organic Chemistry online course is to give the student interested in the health professions an introduction to organic chemistry emphasizing the concepts that will be important for, and provide the basis for, the subjects the student will encounter in his professional studies. This course by Vishwa will give a brief introduction to organic chemistry and some simple organic compound like alkanes, alkenes and alkynes. Textbook: Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition, by Brown, Foote, Iverson, and Anslyn; BrooksCole, 2008, available at the UBC Bookstore Laboratory Materials: Chemistry 203 Laboratory Manual, 1 st edition by Wickenden (includes laboratory notebook pages sold by the Department of Chemistry). The Introduction to Organic Chemistry chapter of this High School Biology Tutoring Solution is a flexible and affordable path to learning about organic chemistry. Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Organic chemistry is the study of living thingsnot in the same way that biology is the study of life. Rather, organic chemistry takes a look at what composes the living things, and how theyre structured.
Related Images:
- Starship Troopers 3 Marauder 2008
- Knock to down
- Free willy 2 1995
- Assassins creed
- The cave 2018
- Daredorm lick bang
- Somewhere only we know keane
- Sniper ghost warrior 2 rip
- 1080 the simpsons movie
- X men the complete age of apocalypse
- Rg mechanics resident evil 5
- State of trance classics
- Reign nl subs
- Up That Black Ass 7
- Roi lion 3 french
- City of go
- S02e03 how its made
- Gta 4 with patch
- Star wars 2 divx
- Real Madrid Bayern Munich
- Mad as hell
- Mac osx bootable
- Super djata band
- Imagine dragons deluxe edition night visions
- House of card nf
- Ui hyeong je
- The talent show
- Disney aladin
- Belly by sandra
- High School English Grammar Composition
- Made in usa
- Its never been like that phoenix
- I got a woman remix
- Out of sight dvdrip
- Peaky blinders 2013
- Dc week 165
- Grown ups 2 brrip nl
- Real steel hd mod
- Nubile films jessa
- Deus e o diabo na terra do sol
- Barcelona real madrid 2006
- Barbie et le palais de diamant
- Channa coke studio
- Embrace gravity
- Video maker pro
- Greek audio
- Windows home classic player
- Dead shadows 2012
- Frequenze pericolose ita
- Fraction of a second
- Drag race s01e
- Cat and bones
- Star wars six
- Download
- Gratitude Diary
- The nutt house
- The misfits earth
- Batman arkham origins ita
- Tomcraft sure shot
- Dangelo how does it feel
- Stravinsky symphony of psalms
- Conter strike 1
- Moody blues strange times
- Survival the cut
- Roupa nova dois acustico
- Born this way live
- True blood extras
- The family prince
- The highlanders touch
- Stock photos sea
- Craig ferguson 2018 05 22
- End of watch dvd 2012
- Digital TV on PC
- Adobe Photoshop CS mac
- Warm bodies italian
- Twilight breaking dawn part 1 hindi 720p
- 2018 texas chainsaw massacre
- All above in
- Paris to berlin
- Grand theft auto s
- Feel the love john
- Sathuranga vettai dvd
- Pinkpop pearl jam